Band 5
(Cellular Band)
A radio frequency band near 850 MHz. It was the first band used for (analog) cellular networks in the U.S., and so was simply called the "Cellular" band. Since then, other bands have been created in the U.S. for cellular networks, such as PCS and AWS.
As the industry moved from analog to digital to 3G, the Cellular band in the U.S. has been used for many different technologies, including AMPS, TDMA, CDMA, GSM, and WCDMA.
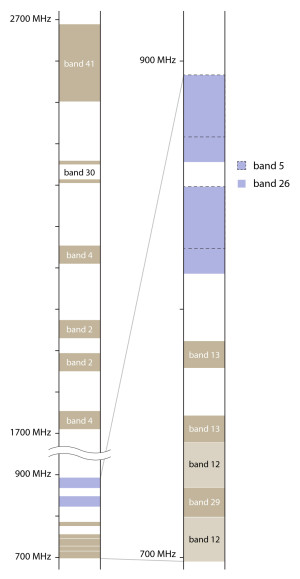
In the context of WCDMA and LTE networks, the Cellular band is also known as band 5 (V). In the context of CDMA networks, it is known as BC0, which stands for band class 0.
The Cellular band is sometimes referred to as the 800 band, 835 band, or 850 band. It is important not to confuse the Cellular band with the different, older ESMR band, which is also called the 800 band. Although both bands are near 800 MHz, the exact frequencies are different and incompatible.
See: ESMR
Band 26 is an extended version of the cellular band that includes the frequencies of band 5, plus some of the lower frequencies that were previously part of the ESMR band. This extended cellular band is used by Sprint for LTE service.
(To make the distinction between Cellular and ESMR, Phone Scoop refers to the ESMR band as 800, and the Cellular band as 850.)
Last updated Feb 7, 2017 by Rich Brome
Editor in Chief Rich became fascinated with cell phones in 1999, creating mobile web sites for phones with tiny black-and-white displays and obsessing over new phone models. Realizing a need for better info about phones, he started Phone Scoop in 2001, and has been helming the site ever since. Rich has spent two decades researching and covering every detail of the phone industry, traveling the world to tour factories, interview CEOs, and get every last spec and photo Phone Scoop readers have come to expect. As an industry veteran, Rich is a respected voice on phone technology of the past, present, and future.



